Comparative Building Costs: Healthcare Buildings
Healthcare Building #1
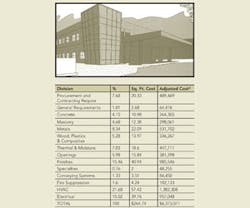
This 24,073-square-foot ear, nose, and throat medical office and surgical center was designed to replace an outgrown existing facility and houses a variety of ENT disciplines within the same facility for patient convenience. The floor plan defines the three main public elements of the building: the entry and lobby areas, the surgery area, and the physician practice area. The facility is fully sprinkled with a fire suppression system.
Foundation: Cast-in-place concrete slab on grade
Exterior: Masonry and EIFS
Interior: Drywall, concrete floors, acoustical ceilings, wall protection, and automatic doors
Flooring: VCT and carpet
Roofing: Membrane roofing system
Healthcare Building #2
This 24,626-square-foot medical mall was designed to provide a variety of medical services under one roof and utilizes design-build construction. The architect selected exterior masonry for energy efficiency and ease of maintenance. Small windows are placed high in the walls, punctuating the façade and bringing in natural light to the medical offices while maximizing patient privacy.
Foundation: Slab on grade
Exterior: Masonry
Interior: CMU and drywall over metal studs
Flooring: Porcelain ceramic tile, carpet, and VCT
Roofing: Metal and membrane system